Writing Paryavaran Pradushan Per Nibandh: Causes, Effects, and Solutions
Environmental pollution stands as one of the biggest global challenges today. Human activities disrupt nature’s balance in pursuit of comfort and needs. Expanding industries, vehicle emissions, rampant deforestation, and excessive plastic use all contribute to this crisis. Understanding paryavaran pradushan per nibandh becomes crucial to grasp the problem and work toward solutions.
According to IQAir’s latest data, India ranks fifth in global air pollution for 2024, with an average PM2.5 concentration of 50.6 µg/m³. The World Air Quality Report highlights that 42 of the world’s 50 most polluted cities are in India. In Delhi, about 11.5 percent of annual deaths link to pollution. Knowing paryavaran pradushan ke karan aur upay helps everyone play a role in curbing this.
Pollution occurs when harmful substances enter the natural environment, affecting air, water, soil, and living beings. This leads to health issues, ecosystem damage, and climate change. A well-structured paryavaran pradushan per nibandh covers types, causes, impacts, and remedies.
Defining Environmental Pollution
Pollution refers to the process where harmful elements mix into the environment, water, soil, or air, posing risks to life and nature. In Hindi, paryavaran pradushan kya hai? It’s the contamination that harms ecosystems.
This issue arises from human interference. Natural elements like air, water, and soil get tainted, leading to widespread consequences. Recognizing this helps in framing effective responses.
What Constitutes Pollution
Harmful gases, chemicals, noise, or energy disrupt the balance. This affects humans, plants, and animals alike.
Historical Rise of the Problem
Industrial growth and urbanization accelerated pollution. Over time, awareness has grown, pushing for action.
Types of Environmental Pollution

Environmental pollution manifests in various forms, each with unique sources and effects. Major types include air, water, soil, noise, light, radioactive, and nitrogen pollution. Addressing them requires targeted strategies.
These types interconnect, amplifying damage. For instance, air pollution can lead to acid rain, affecting water and soil.
Air Pollution Explained
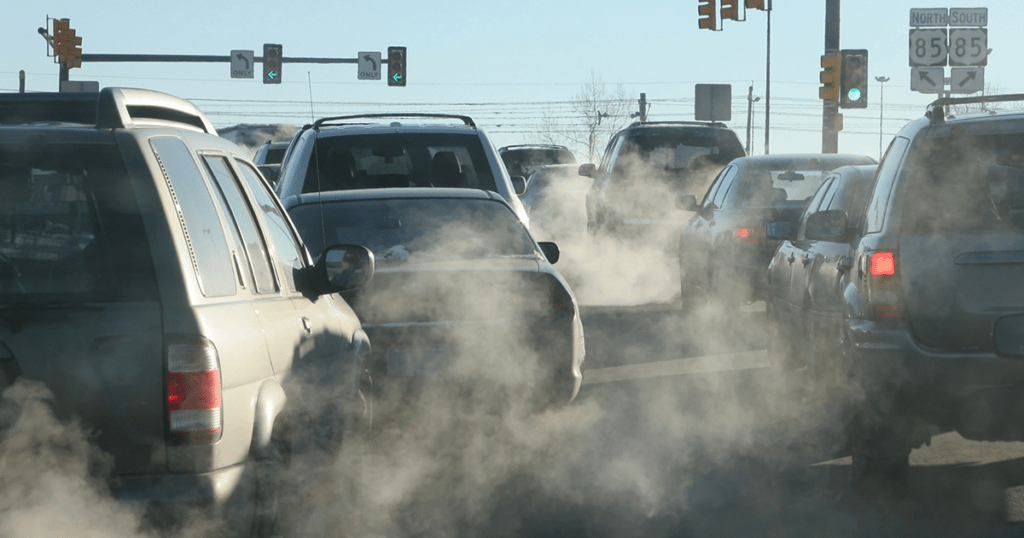

Air pollution, or वायु प्रदूषण, happens when smoke, dust, and gases like carbon monoxide contaminate the atmosphere. Vehicles, factories, and crop burning are key culprits.
This type causes respiratory diseases and reduces visibility through smog.
Prevention Measures for Air
Switch to clean fuels like CNG. Promote electric vehicles and plant trees to absorb pollutants.
Water Pollution Details
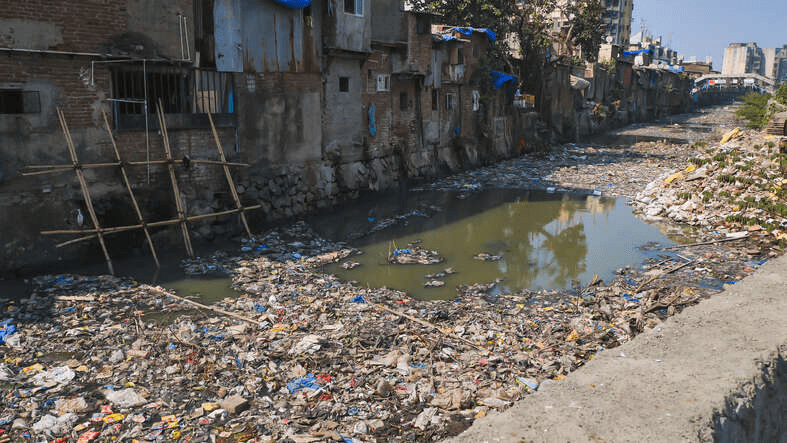
Water pollution, जल प्रदूषण, occurs when chemicals, plastics, or sewage enter rivers, lakes, and oceans. Industrial waste and untreated sewage are major sources.
It leads to waterborne diseases and harms aquatic life.
Causes of Environmental Pollution
Multiple factors drive pollution. Human activities top the list, from industrial emissions to daily waste.
Understanding these helps in mitigation. Pollution doesn’t happen in isolation; causes overlap across types.
Major Sources of Air Pollution
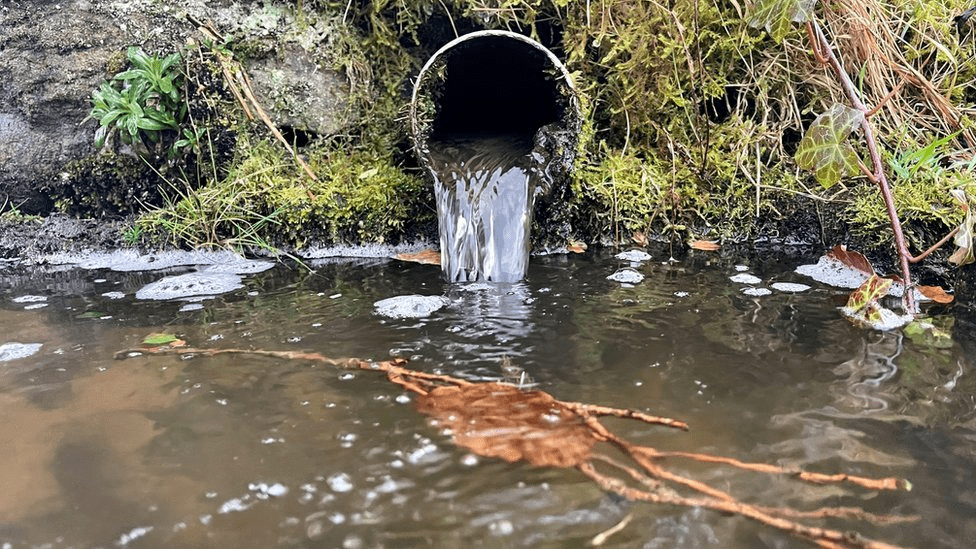

Vehicle exhaust from fossil fuels. Factory smoke and refrigerant gases contribute heavily.
Agricultural pesticides and waste decomposition add to it.
Key Contributors to Water Pollution
Dumping household waste. Sewage and erosion from poor farming practices.
Industrial discharge and oil spills from coastal wells.
Cultural Practices Impacting Water
Immersing idols, flowers, and ashes in rivers during rituals pollutes water bodies.
Effects of Pollution on Health
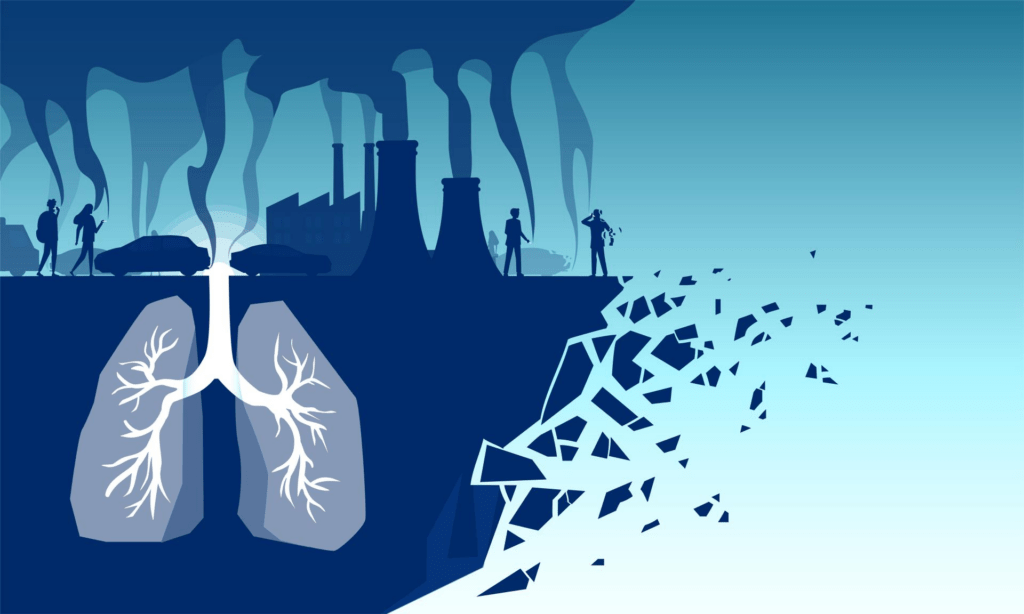
Pollution severely impacts human health. It contaminates air, water, and soil, leading to various ailments.
Air pollution triggers asthma and heart diseases. Water pollution causes diarrhea and typhoid.
Soil pollution contaminates food chains, leading to birth defects and cancer.
Respiratory and Cardiovascular Issues
Inhaling polluted air leads to lung cancer and high blood pressure.
Waterborne Diseases
Contaminated water spreads cholera and hepatitis.
Have you noticed more allergies in polluted areas?
Impacts on Wildlife and Nature
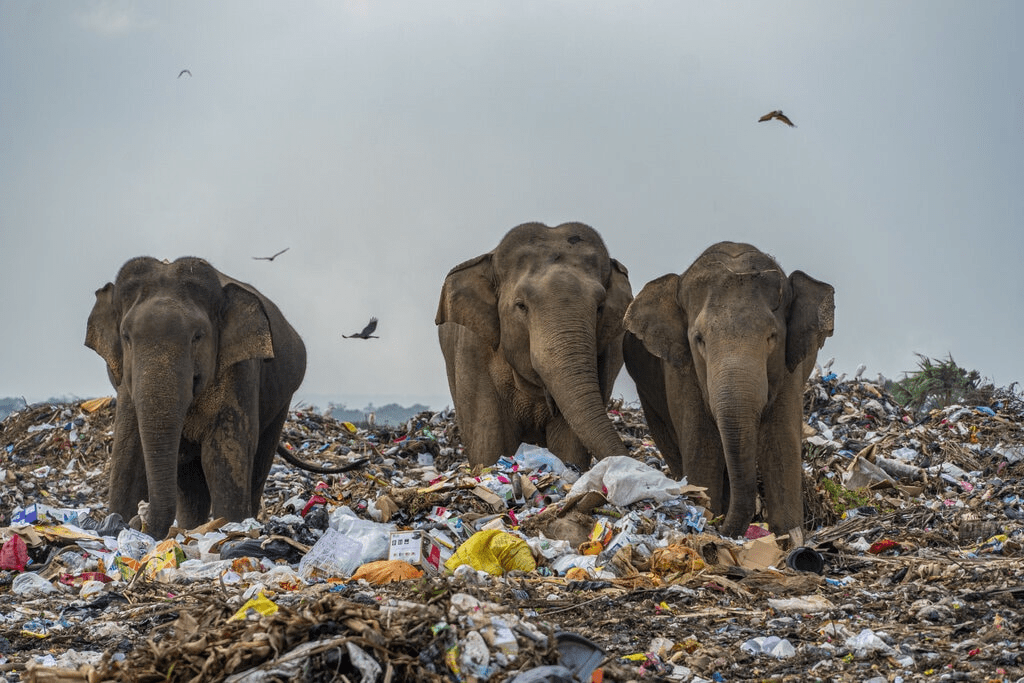

Pollution devastates wildlife. It destroys habitats and causes food shortages.
Animals suffer diseases and become vulnerable to predators.
Natural ecosystems lose balance, affecting biodiversity.
Habitat Destruction
Deforestation and water pollution displace species.
Food Chain Disruptions
Toxins accumulate, harming higher-level organisms.
Soil and Noise Pollution Effects
Soil pollution reduces land fertility. Chemical fertilizers and waste degrade soil quality.
Noise pollution from traffic and machines causes hearing loss and stress.
Both affect agriculture and mental health.
Agricultural Productivity Loss
Polluted soil yields fewer crops. Plants grow stunted.
Mental Health Consequences
Constant noise leads to insomnia and anxiety.
Solutions to Combat Pollution
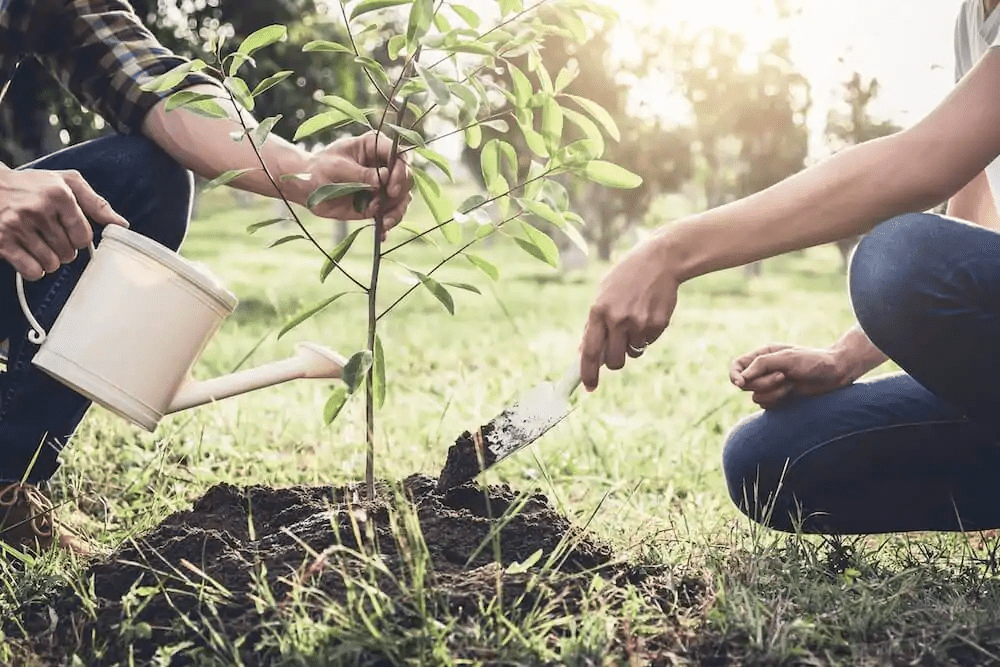

Effective solutions exist. Clean energy sources like solar and wind reduce emissions.
These are renewable and eco-friendly.
Tree planting absorbs carbon and improves air quality.
Adopting Renewable Energy
Use wind, solar, and hydro power. They cut down on harmful gases.
Waste Management Practices
Segregate waste for recycling. Compost organics to enrich soil.
Reducing Plastic Use
Opt for alternatives like cloth bags. Minimize single-use items.
Role of Government and Society

Governments enact policies like the National Clean Air Programme. It aims to reduce pollution in cities by 30% by 2026.
Acts like the Water Pollution Control Act of 1974 regulate discharges.
Society must participate through awareness and compliance.
Key Government Initiatives
Environment Protection Act 1986 safeguards natural resources.
Plastic Waste Management Rules 2016 curb plastic pollution.
Community Involvement
Organize clean-up drives. Educate on sustainable living.
Table of Pollution Types and Remedies
This table summarizes major types with quick remedies.
| Type of Pollution | Main Causes | Key Effects | Simple Remedies |
| Air (वायु) | Vehicle smoke, factories | Respiratory diseases | Electric vehicles, trees |
| Water (जल) | Industrial waste, sewage | Waterborne illnesses | Treatment plants, no dumping |
| Soil (मृदा) | Chemicals, plastics | Reduced fertility | Organic farming, recycling |
| Noise (ध्वनि) | Traffic, machines | Hearing loss, stress | Noise limits, awareness |
| Light | Excessive artificial lights | Sleep disruption | Efficient LEDs, dark zones |
Sample Essays on Paryavaran Pradushan Per Nibandh
Essays vary in length but follow a clear structure. Start with an introduction, discuss causes and effects, then suggest solutions.
Short essays focus on basics. Longer ones dive deeper into examples and data.
100-Word Essay Example
Environmental pollution harms air, water, soil, and sound, affecting humans, animals, and plants. Major causes include industrial smoke, vehicle emissions, plastic waste, and deforestation. Effects range from climate change to rising diseases. To counter this, plant trees, manage waste properly, reduce plastic, and use renewable energy. Clean environment ensures healthy life.
200-Word Essay Sample
Paryavaran pradushan per nibandh highlights growing issues like air and water contamination from factories and sewage. Urbanization and chemical use worsen it. Health suffers with more asthma and waterborne illnesses. Wildlife habitats shrink, disrupting ecosystems. Solutions involve awareness, organic farming, and government policies. Collective action can restore balance.
Expanding to 500 Words
Include statistics like India’s pollution rankings. Discuss radioactive and light pollution for depth.
Radioactive and Light Pollution Overview
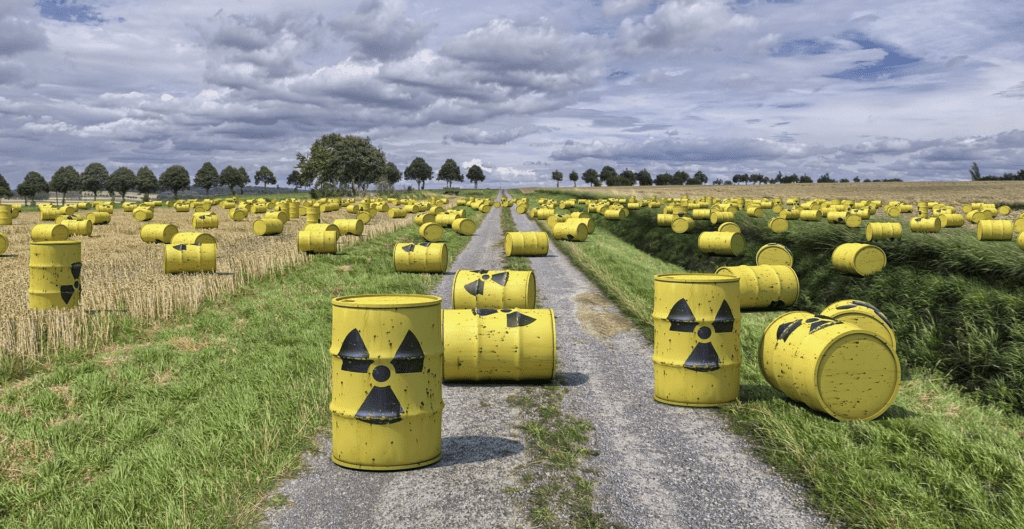

Radioactive pollution stems from nuclear leaks and waste. It causes cancer and genetic defects.
Light pollution from excessive artificial lights disrupts sleep and animal behaviors.
Both require strict safety norms and efficient lighting.
Handling Radioactive Waste
Store securely. Adopt solar alternatives to reduce nuclear reliance.
Managing Light Pollution
Use LEDs sparingly. Create dark sky zones for stargazing.
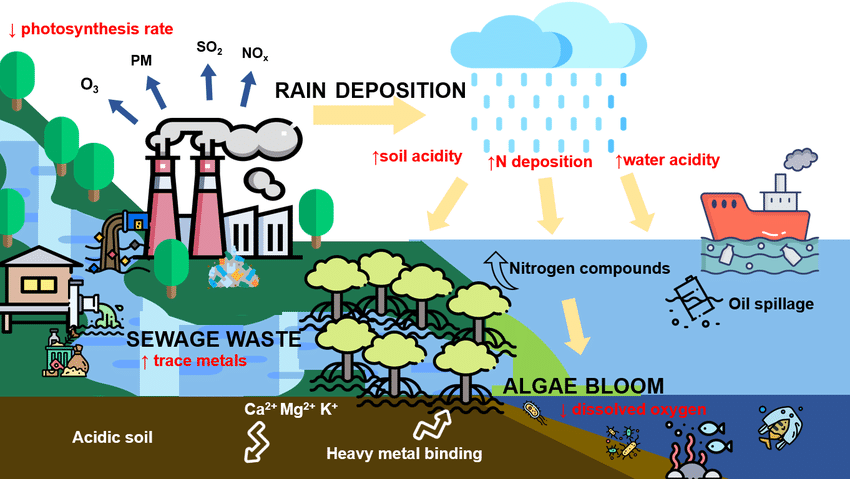
Nitrogen Pollution and Its Challenges
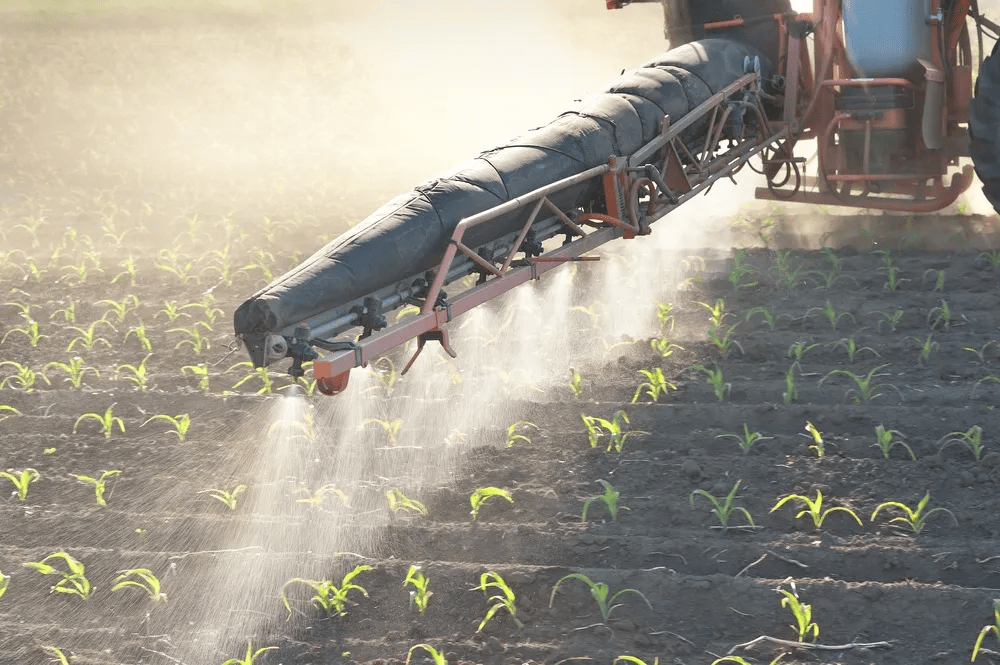

Nitrogen pollution arises from excess fertilizers and animal waste. It leads to eutrophication in water bodies.
Algal blooms deplete oxygen, killing fish. Health risks include blue baby syndrome.
Agricultural Practices Causing It
Overuse of nitrogen-rich inputs. Industrial runoff adds to it.
Mitigation Strategies
Balanced fertilizer application. Natural composts like vermicompost.
What steps can you take in your daily routine?
Author’s Perspective on Collective Action
Everyone must contribute. Small changes like reducing waste and planting trees add up.
Education plays a key role. Teach children about paryavaran pradushan per nibandh to foster responsibility.
Society and government together can enforce cleaner practices.
Individual Responsibilities
Recycle, conserve energy, avoid single-use plastics.
Broader Societal Changes
Promote sustainable development. Support eco-friendly policies.